On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Systems
Thinking about going solar but not sure which system is right for you? There are three types of solar systems installed that are on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems. We have explained all these terms in simple and easy way, so you can make the best choice for your energy needs.
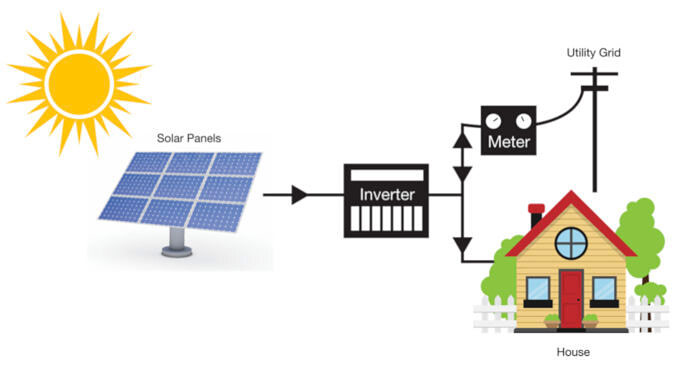
1. On-Grid Solar Systems: Connected to the Utility Grid
An on-grid solar system (also called Grid-Tied) is the most popular type of solar setup, especially in cities and towns. This system is connected to the local electricity grid, so you still rely on your power company. Here’s a simple rundown:
-
How It Operates: During the day, your solar panels capture sunlight and turn it into electricity. If you produce more electricity than you use, the excess energy is sent back into the grid. At night or on cloudy days, when your panels aren’t generating much power, you draw electricity from the grid. It’s a two-way street—you give and take electricity as needed.
- Benefits: The main advantage is net metering. This allows you to earn credits or reduce your electricity bills by selling your extra energy back to the grid. You also have the security of knowing that if your solar system isn’t producing enough energy, the grid is there as a backup.
-
Drawbacks: One downside is that if there’s a power outage in your area, your solar system won’t work unless you have a backup battery. You’re also still somewhat dependent on your utility provider.
This system is great if you want to lower your electricity bills without
cutting ties with the grid completely. It’s an easy and cost-effective way to
make the switch to solar.
2. Off-Grid Solar Systems: Independent and Self-Sufficient
An off-grid solar system is just what it sounds like—it’s not connected to the utility grid at all. You generate all the electricity you need yourself, making you completely independent from your power company. Here’s how it works:
-
How It Operates: Your solar panels produce electricity during the day, which is stored in batteries. These batteries provide power when the sun isn’t shining, like at night or on cloudy days. Since you’re not connected to the grid, your solar system is your only source of power.
-
Benefits: The biggest plus is complete independence. You won’t receive any electricity bills, and you’re not affected by grid outages or rate hikes. This system is also ideal for remote areas where connecting to the grid isn’t feasible.
-
Drawbacks: The main challenge is the cost. Off-grid systems require a battery storage system to ensure you have power when the sun isn’t shining, which can be expensive. If your batteries run out and your panels aren’t generating energy, you could be left without power until the sun returns.
This system is perfect for those who live in remote locations or want to be
completely independent from the grid. If you’re willing to invest in good
batteries, it’s a reliable way to power your home.
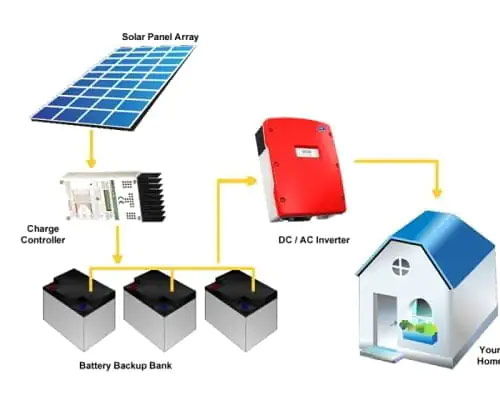
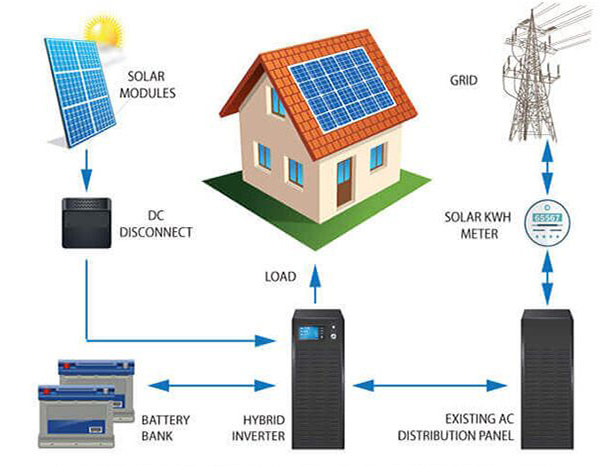
3. Hybrid Solar Systems: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
A hybrid solar system is a blend of on-grid and off-grid systems. This setup connects to the grid while also having battery storage for backup power.
-
How It Operates: Like an on-grid system, your solar panels generate electricity, and any excess power can be sent back into the grid. However, with a hybrid system, you also have batteries that store extra energy. This stored energy can be used during power outages or when the sun isn’t shining, reducing your reliance on the grid even further.
-
Benefits: You get the reliability of the grid and the independence of an off-grid system. You can still take advantage of net metering, and you’ll have backup power during outages. If your batteries run low, you can always draw power from the grid.
-
Drawbacks: Hybrid systems can be more expensive due to the cost of batteries and additional equipment. However, the extra investment often pays off in terms of energy security and flexibility.
This system is ideal for those who want energy independence without
completely cutting ties with the grid. It’s a smart choice for homes in areas
with frequent power outages or unreliable grid service.
Qet a Quote
Get a Free Quote